Geography of Austria is diverse in nature, comprising all major types of topographical features. Austria is mainly a mountainous country with a central location on the map of Europe. With a total land area of 83,859 kilometer square, it is double the size of Switzerland, and surrounded by countries on all sides.
Geography of Austria
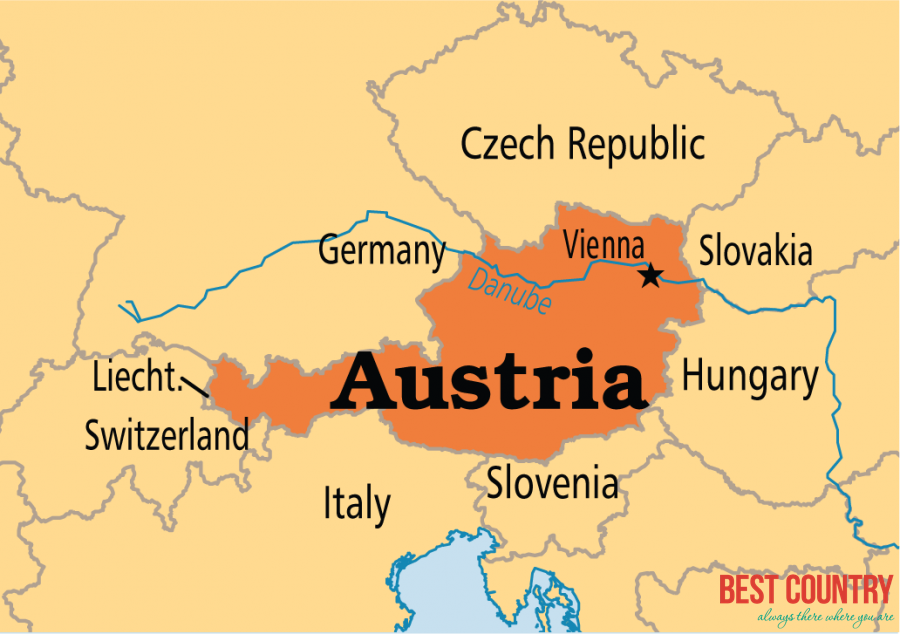 Austria has common natural borders, which it shares with Liechtenstein and Switzerland in the west and Czechoslovakia, Germany and Slovakia in the north. Hungarian province and Slovenia protect the country from the eastern and southern corners respectively.
Austria has common natural borders, which it shares with Liechtenstein and Switzerland in the west and Czechoslovakia, Germany and Slovakia in the north. Hungarian province and Slovenia protect the country from the eastern and southern corners respectively.
The shape of Austria resembles more or less a pear and segregated into three distinct and unequal geographical regions. The largest among these regions consists of the Alps , which cover about 62 percent of the total land area in Austria. To its east, lie a part of the Pannonian Plain and River Danube constitute its northern parts. The hard granite rocks of the Alpine regions are popular among those passionate about highlands.
The Danube River is another important part of the Geography of Austria. Originating near Donaueschingen in south-west Germany, it flows through the Austrian mainland to meet the Black Sea and terminate itself. . Danube is perhaps the only major European river that has an eastward flow. Its water offers extensive transportation facilities to most European countries through inland water routes like Rhine-Main-Danube Canal in Bavaria.
The third significant region in the Geography of Austria is the Bohemian Forest. In reality, it is a range of mountain made up of hard granites, continuously swept by very strong winds. Located in the northern parts of River Danube, these forests include the remaining ten percent of Austria.
Climate is quite significant an issue as far as the Geography of Austria is concerned. The climatic condition in Austria is basically moderate, with Mediterranean winds blowing constantly to make the weather temperate in nature. This maritime climate suffers no precipitation, hence devoid pf humidity. It is due to this annual pleasant climate that travelers can come down to Austria to witness its topographical variations at any part of the year.