The country lies between latitudes 20° and 28°N, and longitudes 72° and 80°W.
Geography of the Bahamas
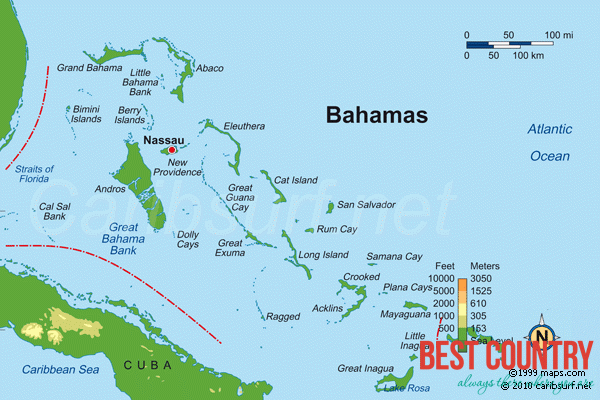 The closest island to the United States is Bimini, which is also known as the gateway to The Bahamas. The island of Abaco is to the east of Grand Bahama. The southeasternmost island is Inagua. The largest island is Andros Island. Other inhabited islands include Eleuthera, Cat Island, Long Island, San Salvador Island, Acklins, Crooked Island, Exuma and Mayaguana. Nassau, capital city of The Bahamas, lies on the island of New Providence.
The closest island to the United States is Bimini, which is also known as the gateway to The Bahamas. The island of Abaco is to the east of Grand Bahama. The southeasternmost island is Inagua. The largest island is Andros Island. Other inhabited islands include Eleuthera, Cat Island, Long Island, San Salvador Island, Acklins, Crooked Island, Exuma and Mayaguana. Nassau, capital city of The Bahamas, lies on the island of New Providence.
All the islands are low and flat, with ridges that usually rise no more than 15 to 20 m (49 to 66 ft). The highest point in the country is Mount Alvernia, formerly called Como Hill, which has an altitude of 63 metres (207 ft) on Cat Island.
To the southeast, the Turks and Caicos Islands, and three more extensive submarine features called Mouchoir Bank, Silver Bank, and Navidad Bank, are geographically a continuation of The Bahamas, but not part of the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.